Tight on Cloud Computing Budget? This Guide Will Help You Optimize Your Spending!
Key Factors Impacting Enterprise Cloud Spending in 2024
In 2024, enterprises are expected to witness significant changes in their cloud computing expenditure, driven by several emerging trends and strategic priorities. Below are the key factors influencing cloud spending in the coming year:
1. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies:
More enterprises are adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize cost and performance across different platforms. By selectively choosing cloud providers, businesses can tailor solutions to meet specific operational needs while finding the most cost-effective services available. This flexibility allows companies to balance workloads across different environments, enhancing cost management.
2. Automation and Intelligent Management:
As cloud services grow more complex, enterprises will increasingly rely on automation tools and intelligent algorithms to manage resources efficiently. These technologies can help businesses make smarter decisions through real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, ultimately reducing cloud expenditures. Automation reduces human errors and minimizes manual intervention, optimizing resource usage.
3. Compliance and Governance Optimization:
Enterprises are placing a stronger emphasis on cloud compliance and governance, especially in data privacy and security. Investing in compliance solutions and governance frameworks helps organizations avoid potential fines while driving long-term financial benefits by creating more efficient cloud management systems. Proactive management of regulatory requirements ensures smooth cloud operations without unexpected costs.
4. High Availability and Security Features:
Modern enterprises now expect that cloud services, such as storage, come with built-in high availability and security features as part of the standard package. Previously, services like policy management, identity management, and monitoring were considered add-ons. However, providers are now facing pressure to integrate these functionalities into their basic offerings, making them more attractive without additional charges.
5. Resource Utilization Efficiency:
Companies are increasingly unwilling to pay for unused resources, making efficient resource allocation a top priority. Ideal cloud service providers offer solutions that automatically scale computing instances up or down during peak and off-peak times. The ability to consolidate core units in CPUs and reduce the risk of over-provisioning will be critical for enterprises looking to avoid unnecessary costs.
6. Dynamic Pricing Models:
As competition in the cloud computing market intensifies, more cloud providers are introducing dynamic pricing models to attract users. This allows businesses to temporarily rent resources based on real-time demand, providing flexibility and helping reduce fixed expenditures. Dynamic pricing aligns cloud costs with actual usage, offering more control over expenses.
7. Environmental Sustainability Considerations:
More enterprises are becoming mindful of the environmental impact of their cloud services and are seeking providers that offer green cloud computing solutions. Not only does this align with compliance standards, but it also enhances the company’s corporate social responsibility image. Over time, choosing sustainable cloud options could lead to improved cost efficiency as energy-saving technologies continue to evolve.
8. Continuous Usage Optimization:
To minimize wasted costs, businesses must continuously review and optimize their resource usage. This requires full visibility into their cloud infrastructure, including identifying idle instances and orphaned storage volumes and rightsizing oversized instances according to actual workloads. Ongoing optimization efforts are crucial for controlling cloud expenses over time.

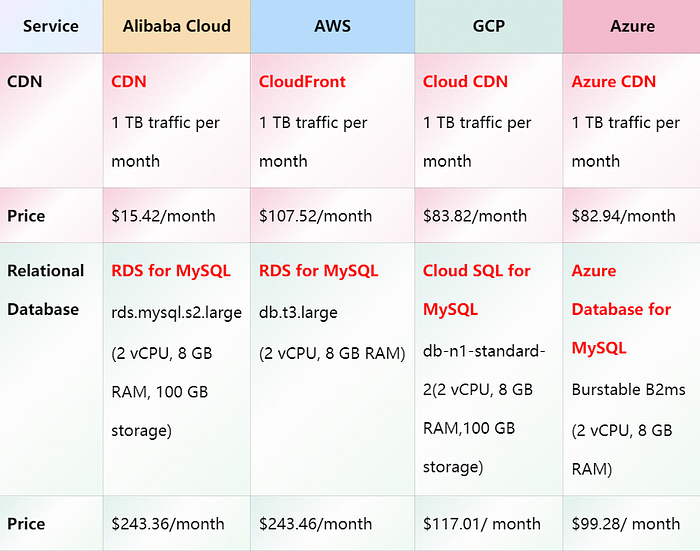
Note: The above pricing data is based on the latest information as of September 2024. Actual prices may vary depending on region, service options, and usage. For the most accurate pricing, please visit the respective cloud service providers’ official websites.
How Do Enterprises Evaluate Cloud Costs?
To accurately evaluate cloud costs, companies must conduct in-depth research based on various factors such as service type, workload, compute demand, billing models, data transfer fees, security compliance costs, and operational management expenses. A comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis is essential to ensure accurate and effective cost estimation. Through careful planning and management, enterprises can control cloud computing costs while maximizing the benefits of cloud technology.
1. Choosing the Right Service Type:
Different types of cloud services — Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) — have varying pricing models. IaaS typically charges based on usage, requiring enterprises to assess their computing, storage, and network needs. PaaS and SaaS may use subscription models, which require careful evaluation to ensure cost-effectiveness.
2. Billing Models:
Enterprises must pay attention to the billing models offered by cloud providers. Common models include pay-as-you-go, prepaid, and long-term contracts. While pay-as-you-go is flexible, it can lead to cost spikes during peak demand. Prepaid and long-term contracts may lower unit costs but require accurate predictions of future needs to avoid wasted resources.
3. Data Transfer Fees:
Cloud costs are not limited to storage and computing; data transfer fees also play a significant role. Many cloud providers charge for outbound data traffic, so companies need to consider the frequency and volume of data flow when designing system architectures to estimate potential costs.
4. Security and Compliance Costs:
Security and compliance are critical cost factors when using cloud services. While many providers offer basic security measures, companies may need to invest in additional security tools such as encryption, identity management, and compliance audits. These extra expenses should be factored into the overall budget.
5. Operational and Management Costs:
Even with cloud services, enterprises still need to allocate resources for operations and management. This could involve hiring cloud experts to manage environments or dedicating time to application and data migration. These operational costs directly impact overall cloud spending.
6. Potential Savings and Benefits:
While cloud computing entails costs, companies must also evaluate the potential savings and benefits it offers. For example, cloud scalability enables businesses to adjust resources as demand increases, avoiding the high maintenance costs of traditional IT infrastructure. Additionally, cloud services offer greater flexibility and faster market responsiveness, which can translate into financial gains.
7. Cost Optimization Tools:
Many cloud providers and third-party companies offer cost optimization tools to help enterprises monitor and analyze cloud usage. These tools provide detailed reports on resource consumption, helping businesses identify waste and inefficiencies to make necessary adjustments and reduce overall costs.
Cloud Computing Cost Comparison: Alibaba Cloud vs. AWS, Azure, and GCP
IDC predicts that by 2027, global public cloud services spending will reach $1.35 trillion, driven by demand for digital transformation and technologies like machine learning and generative AI. Below is a detailed cost comparison of major cloud providers as of Q3 2023:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a range of pay-as-you-go services, including virtual instances and storage. AWS Outposts also offers limited private cloud products but lacks usage-based pricing or SLAs. A VM instance with four vCPUs and 16 GB memory running 744 hours per month costs approximately $100.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP provides on-demand, committed use, and bulk discount pricing, with a similar VM configuration costing around $99 per month. GCP does not offer managed Oracle database services.
Microsoft Azure: Azure offers a wide range of cloud services with pay-as-you-go and reserved pricing models. A comparable VM instance costs about $134 per month, with potential savings of 32% to 55% through reserved pricing.
Alibaba Cloud: Alibaba Cloud offers a comprehensive suite of on-demand cloud services, including virtual machines, storage, and specialized products. For a virtual machine instance with 4 vCPUs and 16 GB of RAM running 744 hours monthly, the estimated cost is around $54. Additionally, Alibaba Cloud provides flexible pricing models and discounts based on commitment levels, allowing businesses to optimize costs effectively. The platform supports various deployment options, including hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, catering to diverse enterprise needs. With a strong focus on security and compliance, Alibaba Cloud also integrates advanced features to enhance performance and reliability.

